Exploring Agentic Desktop Control: A Comparison of Manus AI and OWL’s Features, Performance, and Limitations
Learn how agentic desktop control simplifies workflows with one command, see if Manus AI or OWL leads in boosting productivity.
4/23/2025
artificial intelligence
18 mins

The world today is witnessing innovative advancements, especially after the introduction of AI agents. The applications of these AI agents aren't just ensuring convenience, but its speeding up and completing many complex tasks that would require a lot of effort manually. The need for convenience has now extended up to automated desktop control, leading to the introduction of an AI agent-driven desktop control solution.
With Agentic desktop control, industries can be facilitated with an automated tool to get their routine task done easily. From searching the internet to making a document, creating an Excel sheet, or designing a presentation with agentic desktop control, you can get these tasks done from a single prompt.
With our article, we will help build an understanding of how this agentic desktop control solution works. Here, we will particularly discuss Manus AI and OWL, compare their features, performance, and limitations.
What is Agentic Desktop Control?
Agentic desktop control is an AI-driven agent that automatically interacts and controls desktop environments, It facilitates the user by performing tasks on various applications without human involvement
These desktop control agents act as intelligent digital assistants by opening software, navigating user interfaces, using user inputs, and reading the screen content to complete the assigned task.
This agentic desktop control solution is a fusion of different technologies that includes large language models, robotic process automation (RPA), and computer vision. Combining these essential methodologies provides an automated approach for getting a specific task executed under a single instruction without the interference of any human.
Manus AI vs OWL
Below, we have provided you with an overview of the comparison between Manus AI and OWL. This table highlights the core differences, focusing on aspects, features, and limitations, which will help you understand their difference more easily.
| Aspect | Manus AI | OWL |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Proprietary tool | Open Source Framework |
| Source Code Access | Not available | Publicly accessible |
| Developer | Monica ( Chinese Startup) | Creator of OpenDevin |
| Availability | Limited to public access | Free available on GitHub |
| Execution Environment | Cloud-based only | It can work on multiple OS like Windows, macOS, and Linux |
| Architecture | Multi-agent system integrated with LLMs like Claude 3.5 and Qwen | Vision-language interface with action abstraction layer and feedback loop |
| Task Handling | High-level autonomous execution (data analysis, coding, reporting, automation) | Visual UI interaction, file navigation, input simulation |
| Memory Support | Stateful memory for managing ongoing and multi-step workflows | Session memory for tracking previous interactions and task planning |
| Tool Integration | Built-in support for browsers, code editors, and databases | Plug-and-play LLM & CV backends like GPT, Claude |
| Use Base | Aimed at professionals, non-tech users, and businesses | Designed for developers, researchers, and automation enthusiasts |
| Hands-free Operation | Yes – performs complex tasks from a single instruction | Yes – works in perception → reasoning → action loop |
| Error Recovery | Not explicitly mentioned | Lacks robust error recovery; task restart may be needed on failur |
| Security | Risky due to full cloud access and lack of transparency | Risky without sandboxing; agent has system-level control |
| Language support | Limited regional language support | Language flexibility depends on an integrated LLM |
Manus AI vs OWL
We have further explained both the Manus AI and OWL framework for agentic laptop control in detail in this article, which will explain to you the methodology, features, and limitations of both these solutions individually.
Manus AI
Manus AI is an autonomous tool developed by the Chinese startup Monica that can control your desktop activity based on your provided instructions. This is an agentic AI-driven tool that doesn’t require continuous input like previous AI methodologies.
Manus AI acts as an agent that single-handedly handles the planning and execution of complex tasks across various domains with reduced human involvement. It's a proprietary system that is currently under development and deployment, it has limited public access to its architecture or source code
This agentic desktop control tool allows users to perform data analysis, report generation, workflow automation, and code development through a single input. By introducing these major advancements, Manus AI is making a significant contribution to reducing the gap between intent and execution. Thus, it efficiently reduces the time in turning your idea into a real work.
Example Use Case of Manus AI
To experience Manus AI's performance, we asked it to perform job hunting for an entry-level software engineering role. Instead of doing everything manually, we asked Manus AI to search online for open positions, extract key info (company, job title, location, skills, application link), and neatly format it into an HTML page saved on your desktop.

Methodology Behind Manus AI
Manus AI is not an ordinary AI agent-driven tool, but it has immense potential to revolutionize industries with its diverse applications. But before moving towards discussing its features, let us explain to you the methodology that is working at the backend to execute the tasks automatically over your desktop on user instruction. Below, we have discussed the key elements of the methodology involved in Manus AI that help it deliver the required functionality.
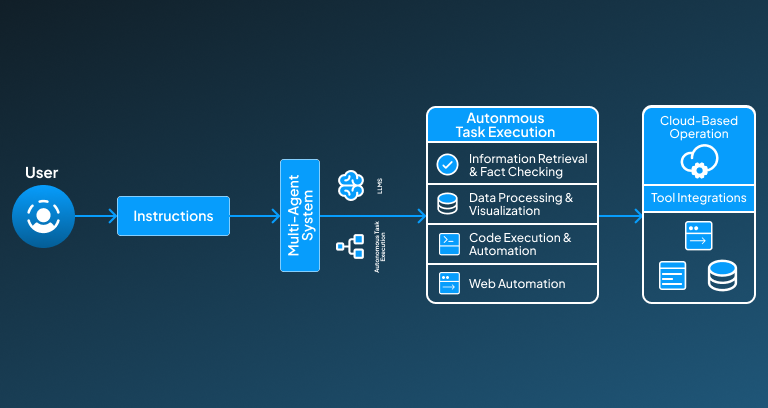
Multi-Agent System Architecture
Manus AI performs the agentic desktop control through the multi-agent architecture that works behind it. This multi-agent system integrates multiple AI models, each of which handles its task individually. This multi-agent architecture allows Manus AI to plan, implement, and refine tasks without the continuous need for human interruption. Each of the AI models under this multi-agent architecture performs its dedicated role while allowing Manus AI to execute a wide range of functions, ultimately enhancing its efficiency.
Integration with Large Language Models (LLMs)
Manus AI has some LLMs integrated into it that provide the foundation for it. It has incorporated LLMs like Anthropics Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Alibaba’s Qwen, which help it provide the required functionality. These LLM models allow Manus to build its understanding and general capabilities to process the provided complex instructions and eventually plan and generate a suitable action for the query.
Autonomous Task Execution
Where traditional AI assistants require step-by-step instructions to execute a task, Manus AI can automatically perform a multi-step task under a single instruction. The following are the steps it goes through at a higher level after receiving an instruction from a user:
- Information Retrieval and Fact-Checking:
In this step of autonomous task execution, it accesses and verifies the data from online sources to validate its factual accuracy.
- Data Processing and Visualization:
After collecting the required data from the sources, it processes it and further creates dashboards to visualize the collected data.
- Code Execution and Automation:
Then, after understanding and analyzing the data, it writes, tests, and deploys code to automate processes
- Web Automation:
Further, as per user instructions, it executes further actions like interacting with web applications, filling forms, and scraping data.
Cloud-Based Operation with Stateful Memory
Manus AI works in a cloud-based environment that allows it to execute tasks smoothly, even when users are not actively involved. It integrates a stateful memory that makes sure to maintain the continuity of ongoing tasks, enabling to execution of complex workflows with minimal interruption.
Advanced Tool Integration
Manus AI integrates some external tools and systems that enable it to perform diverse tasks. These tools allow it to perform all the user-desired tasks while automatically controlling the desktop.
- Web Browsers:
Manus AI integrates a web browser in its solution so that it can fetch real-time information available on the web as per the user's requirement.
- Code Editors:
Manus AI also incorporates code editors to get all the coding tasks executed as per the user's instructions.
- Database Management Systems:
Manus AI also implements database management systems that allow it to handle structured data as per users' needs.
This integration enhances its ability to control tasks on desktops that require interaction with various software, platforms, and applications.
Features of Manus AI
This Manus AI agentic desktop control is making life easy by helping professionals, students, teachers, and people from any field to get their redundant tasks done with a single instruction. So that they can exercise their energies and intelligence over aspects that AI can not perform, ultimately saving time and resources. Below, we have mentioned some of the key features that Manus AI is contributing:
Hands-Free Automation
Manus AI is eliminating the need to provide constant instruction to get your task done over a desktop; with its automation, it handles the entire workflow. Whether you want to get a report prepared by it, or you want a dashboard, or you want it to prepare your documents or scripts, it will complete all the tasks of this nature on your instructions. It won't require your step-by-step instruction to know how to perform the task, as it can figure it out on its own and generate intelligent actions.
All-in-One Workspace
Manus AI allows user to get all their task on a single platform. Instead of exhausting the user to juggle between multiple platforms and applications, it is a platform that enables the user to write, test, and deploy code, extract data from websites, generate documents, presentations, or balance sheets under one roof. It is just like fusing a developer's IDE, research assistant, and productivity suite in a single interface.
Real-Time Web Interaction
With the Manus AI agentic desktop control tool, users can actively extract all the required information from a website by making interactions just like humans do. In this way,y it can perform the web scraping task to gather information like pricing and can even fill out forms and applications on behalf of the instructor with updated information.
Memory-Driven Project Management
Manus AI has a built-in project memory, enabling it to remember the context of all the tasks, instructions, and outcomes that have been achieved with this tool. This implies that it can manage ongoing as well as paused tasks without repeating the steps, making it ideal for managing multi-day projects and complex tasks.
Developer & Non-Developer Friendly
Manus AI is an agentic desktop control tool for everyone, as it adapts to individuals' skill levels. Developers can instruct it to perform specific programming tasks and get it done by consuming less time. Also, non-tech users can provide their instructions to get tasks like content generation or data analysis done without requiring prior in-depth technical knowledge.
Limitations of Manus AI
While Manus AI is introducing transforming advancements that are uplifting the quality of tasks and productivity, eventually, it does hold its own set of limitations. We have discussed some of the limitations below to help you get a better understanding of Manus AI.

Not Open Source
Manus AI is a proprietary agentic desktop control tool, which means that its codebase and internal architecture are not available to the public. This raises limitations around its transparency, customized modifications, and developer collaboration as compared to open-source solutions.
Limited Public Access
Manus AI is not publicly available for everyone's use. This restricts its access, which becomes challenging for individuals and huge business industries who want to experiment with working on this to integrate it into their daily workflows.
No Local Execution
Manus AI works completely in the cloud and doesn't have a localised version. This can be reason of major concern for business organizations and individual users who are handling sensitive information or working in a low connectivity environment.
Experimental Stability
Manus AI is still evolving, therefore, it still exhibits some bugs, missing features, and inconsistency in behavior for some particular workflows. At this stage, it might show compromised action for extremely complex instructions. However, it can easily handle everyday tasks.
Language and Regional Limitations
While Manus AI is still supporting some major languages, it might demonstrate compromised performance for specific regional dialects or languages. It integrates models trained for some specific languages. Therefore, it can only understand instructions provided in those languages to generate a particular action.
OWL
OWL (Optimized Workforce Learning ) is an agentic desktop control open source framework that allows automatic AI agents to interact with desktop environments both visually and functionally. This agentic desktop control framework is introduced by the developer of OpenDevin.
OWL enables AI to control desktop applications by performing the required mouse movements, keyboard inputs, file navigation, and user interface interactions, with or without an API. OWL is bridging the gap between AI reasoning and lower-level human interaction, eventually increasing productivity.
As OWL is an open-source framework, it can easily be accessed by developers, researchers, and business organizations who want to further experiment and build more customized and futuristic desktop control automations with this.
OWL Basic Code Snippet
# run.py
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from camel. models import ModelFactory
from camel. toolkits import (
WebToolkit,
SearchToolkit,
)
from camel.types import ModelPlatformType, ModelType
from camel.logger import set_log_level
from utils import OwlRolePlaying, run_society
load_dotenv()
set_log_level(level="DEBUG")
def construct_society(question: str) -> OwlRolePlaying:
"""Construct a society of agents based on the given question."""
# Create model
model = ModelFactory.create(
model_platform=ModelPlatformType.OPENAI,
model_type=ModelType.GPT_4O,
model_config_dict={"temperature": 0},
)
# Configure toolkits (only web-related tools for your specific question)
tools = [
*WebToolkit(headless=False, web_agent_model=model, planning_agent_model=model).get_tools(),
SearchToolkit().search_google, # Assuming you have Google Search configured
]
# Configure agent roles
user_agent_kwargs = {"model": model}
assistant_agent_kwargs = {"model": model, "tools": tools}
# Configure task
task_kwargs = {"task_prompt": question, "with_task_specify": False}
# Create society
society = OwlRolePlaying(
**task_kwargs,
user_role_name="user",
user_agent_kwargs=user_agent_kwargs,
assistant_role_name="assistant",
assistant_agent_kwargs=assistant_agent_kwargs,
)
return society
def main():
"""Main function to run the OWL system with an example question."""
question = '''
job hunting for an entry-level software engineering role in U.S and save in html file.
Always use a web browser for Google search.
No need to verify your answer..
'''
society = construct_society(question)
answer, _, _ = run_society(society) # Ignore chat_history and token_count
print(f"Answer: {answer}") # Simplified output
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Example Use Case of OWL:
To witness OWL’s performance, we asked OWL to perform the same task of finding out entry-level software engineering roles. Under this task, the tool should automatically search for all the relevant information and list these jobs in html page that should contain the company name, job title, location, skills required, and application link.

Methodology Behind OWL
Behind OWL’s agentic desktop control framework, there is a combination of AI models that enable it to contribute the required functionality. We have mentioned some core elements that are working closely behind OWL to make users' lives convenient:
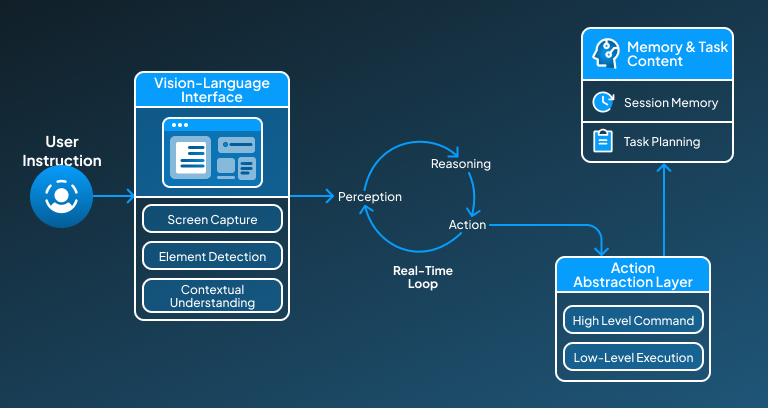
Vision-Language Interface
OWL vision-language interface working at the core of it, this allows AI agents to observe and build it understanding around a desktop environment as humans would perceive it. This helps this framework get familiar with the environment it is working with. This visual language interface helps OWL in providing:
- Screen Capture:
OWL captures the screenshots or video frames of the current desktop view to build an understanding of the overall view.
- Element Detection:
It exercises computer vision techniques like OCR or image segmentation to find and differentiate the visual elements like buttons, icons, input fields, and text present within the provided screen space.
- Contextual Understanding:
After segmenting and classifying the elements within the provided desktop, it passes this information to the agents. This passed information is then further utilized by LLMS for reasoning and generating actions for users' instruction.
Action Abstraction Layer
Now, further in OWL’s framework, we have an action abstraction layer that functions as a control bridge between AI’s decisions and the physical interaction it eventually makes within the desktop.
- High-Level Commands:
This abstraction layer enables the OWL framework to perform higher-level command tasks like “click the submit button” or “type the email in the given field”.
- Low-Level Execution:
With the abstraction layer, OWL can effectively translate the intelligent plan into low-level action by executing the actual mouse movements, keyboard strokes, or drag-and-drop actions using system-level libraries (e.g., PyAutoGUI or OS-specific APIs).
This abstraction layer ensures that agents don’t need to know operating system-specific commands to implement execution; they simply explain the intent behind the instruction, whereas OWL handles execution.
Environment Loop (Perception → Reasoning → Action)
OWL framework functions in a continuous feedback loop, which very much mimics the way of human decision-making. Its decision-making loop has some particular elements that work closely to help OWL in generating dynamic actions.
- Perception: Capture screen and detect elements.
- Reasoning: Pass the environment description to the AI agent (e.g., an LLM or multi-agent system).
- Action: The agent outputs the next action, which is executed.
- Repeat: Owl updates the screen state and continues the loop.
This real-time feedback loop allows agents to make decisions and adapt to unexpected changes within the desktop environment.
Memory and Task Context
OWL framework can store stateful memory, allowing agents to remember previous actions, be able to track progress over a task, and perform complex tasks reliably. By retaining the memory, OWL can significantly improve the interactions being made in the desktop environment.
- Session Memory:
By maintaining the session memory, OWL keeps a record of all previous interactions made within a single session, which can later be resumed as per user requirements.
- Task Planning:
By utilizing the session memory, agents can further plan the workflows, accordingly break them into subtasks, and eventually implement them iteratively.
Features of OWL
OWL agentic desktop control framework has its specific features, which help users across various domains, like developers, researchers, or even casual users, to get their tasks done through an automatic agent. Below, we have mentioned some prominent features of OWL:
Open-Source and Extensible
OWL framework is a completely open-source project, which means it is publicly accessible. Therefore, it allows developers and researchers to access its codebase and the underlying architecture. This makes this framework open to developers to make further customizations as per their specific needs and integrate it with their desktop environment.
Human-Like UI Interaction
OWL framework has AI agents, which make interactions just like how humans would do it. It moves the cursor for clicking, types texts, performs scrolling, and switches apps without particularly needing an API for it.
Vision-Language Pipeline
OWL agentic desktop control framework combines screen capture with a natural language description to help the AI agents build their understanding around the screen context to make more intelligent decisions with increased accuracy and adaptability.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
OWL framework allows its users to benefit from this agentic AI-driven desktop control tool across major desktop operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, but its capabilities may vary depending on the platform. This enhances its usability and accessibility in various environments.
Plug-and-Play AI Integration
OWL framework allows its users to integrate it with multiple large language models or computer vision backends. This allows you to pair it with other open-source tools like OpenAI GPT or Claude to get a more personalized experience.
Limitations of OWL
While OWL is providing amazing automation with its open-source agentic desktop control framework, it does show some limitations in terms of performance. We have listed some of the limitations of the OWL framework to provide you with a complete overview:

Still in Early Development
OWL is a new framework that is evolving continuously. Therefore, it might have some bugs or missing features, which could be critical for production-level use in large-scale enterprises.
Limited Error Recovery
This OWL framework lacks a rollback or error-handling mechanism. So if the AI agent mistakenly takes a wrong action like clicking the wrong button or element, or closing the essential video, then recovery from failure might require manual intervention or require the task to restart.
Vision-Only Dependency
As the OWL framework shows a huge dependency on visual perception, like screen captures or video framing, it might struggle with identifying hidden elements in poorly contrasted user interfaces or dynamic layouts. This aspect impacts its reliability, especially in highly variable or cluttered screens.
Security and Trust Concerns
Providing an AI agent access to control the desktop comes with serious security risks. As these AI agents might interact with sensitive data or change the system's settings. Without implementing strict sandboxing, this can cause damage to your system.
High Resource Usage
For running OWL with a vision pipeline and LLM in a feedback loop, you need to have enough resources within the machines. As this might compromise the performance or restrict the multitasking for lower-end systems.
Applications of Agentic Desktop Control
These agentic desktop control tools can significantly enhance business performance. With its implementation, it can reduce the cost and optimize the workflow significantly. Below, we have listed some major areas where the application of agentic desktop control can drive both productivity and growth for businesses:
Enterprise Workflow Automation
Agentic desktop control tools like Manus AI and OWL can majorly optimize the repetitive and time-consuming workflows for enterprises. By implementing a tool like this enterprise can get its daily redundant tasks like data entry, report generation, form filling, and email drafting done automatically. As this tool can efficiently handle ERP or CRM platforms, it increases the efficacy of everyday tasks with minimal human input.
Software Development and IT Operations
These agentic desktop control tools can also be used to assist the daily work needs of software developers. This tool can assist them in performing tasks like coding, setting up CI/CD pipelines, managing deployments, or analyzing logs for proactive system monitoring. With this integration, software houses will not only experience acceleration in their development cycle but will also reduce the workload on their technical team, allowing them to focus more on innovation and problem-solving.
Data Analysis and Research
An agentic desktop control tool has great potential to help the researcher and analyst. As it can help in sharing their research load by automatically collecting, processing, and creating dashboards to enhance its visualization on a single instruction provided by the user. By handling tasks of this nature, agentic desktop control is making the execution of tasks easier for both technical and non-technical users, as per their specific needs.
Conclusion
Manus AI and OWL are two different yet complementary methodologies for agentic desktop control. Here, Manus AI emphasizes more on precision and technical depth to allow developers to define specific agents using YAML and Python scripts. This makes it go-to tool for users who want customization and detailed task automation, especially within local environments.
On the other hand, the OWL framework focuses on ensuring simplicity and user-friendliness through natural language prompts. With its intuitive experience and open-source access, it allows developers to further tailor it to fulfill their daily needs, allowing users to get their tasks done automatically in their desktop environment.
Eventually, both tools will indicate advancements in human-computer interaction. In the future, whether you want code-based customization or natural conversation, they will offer users increased autonomy and efficiency. So, the decision of choosing between them is reliant on the user's technical comfort, desired use cases, and preference for control versus convenience in shaping their computing workflows.
Do you want AI to revolutionize and speed up your everyday workflow with a single instruction? Feel free to discuss your idea with our experts at Centrox AI and begin your journey toward the tech revolution.

Muhammad Haris Bin Naeem
Muhammad Harris Bin Naeem, CEO and Co-Founder of Centrox AI, is a visionary in AI and ML. With over 30+ scalable solutions he combines technical expertise and user-centric design to deliver impactful, innovative AI-driven advancements.
Do you have an AI idea? Let's Discover the Possibilities Together. From Idea to Innovation; Bring Your AI solution to Life with Us!
Your AI Dream, Our Mission
Partner with Us to Bridge the Gap Between Innovation and Reality.
